Rising energy prices and their impact on the manufacturing industry
The increase in energy prices throughout 2021 as a result of the combination of the sharp rise in global energy demand (due to the reactivation of the economic cycle after Covid) and a certain weakness in supply (due to geopolitical problems and the change in the energy model towards non-fossil fuels) has led to a global energy shock. In 2022, the geopolitical context is putting extra pressure on international gas and oil prices, which could aggravate the already significant impact of the energy bill on manufacturing industry.
Energy prices vary significantly between countries. Retail electricity tariffs for industry are higher on average in the EU than in the US, Canada, Russia, China and Turkey (though lower than in Japan and Brazil).
In energy-intensive industries, these extraordinary increases are having a profound impact on production costs, which have risen by almost 50 percent in some sectors. The situation is likely to be prolonged. Futures markets are pricing European gas at twice or three times their 2021 levels for at least the next three years. Companies in these sectors face an urgent need for action. They must ensure the viability of their businesses today and find ways to maintain or extend their competitiveness for the future.
The implementation of carbon cost
Under a carbon tax, the government sets a price that emitters must pay for each ton of greenhouse gas emissions they emit. Businesses and consumers will take steps, such as switching energy sources or adopting new technologies, to reduce their emissions and lower the impact of the tax. The EU’s emissions trading system (ETS) sets a price on carbon for power plants and industry as well as for flights within the EU.
However, this is a fact that many industrial sectors in the EU are exposed to competition elsewhere in the world. While carbon pricing initiatives are beginning to spread globally (57 have been implemented or are scheduled for implementation, covering a total of 11 Gt CO2-equivalent), these schemes vary in their stringency and scope.
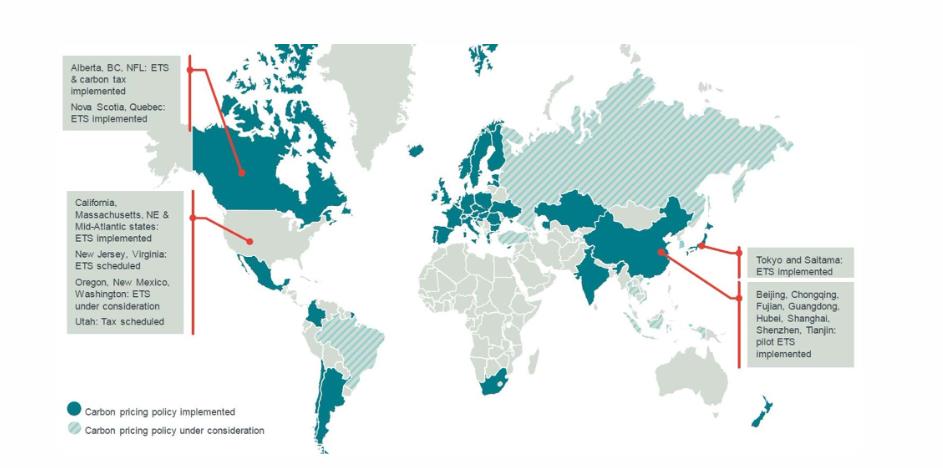
Map of carbon taxes and emissions trading systems (Photo Credit: World Bank)
Carbon Border Adjustment Mechanism (CBAM) Is a process which effectively calculate the sustainability of products based on the involved carbon emissions. The legislative process on the adoption of the CBAM is validated and is becoming a reality for most EU based businesses which are importing and exporting goods around the world.
Machine tool energy consumption needs to be measured efficiently
Machine tools consume enormous amount of energy during machining, build-up to machining, post machining and idling condition to drive motors and auxiliary equipment in the manufacturing system. Reduction of energy consumption during the machining phase is extremely important to improve the environmental performance over the entire life cycle as this is where the impact on energy consumption/CO2 emissions is the highest one.
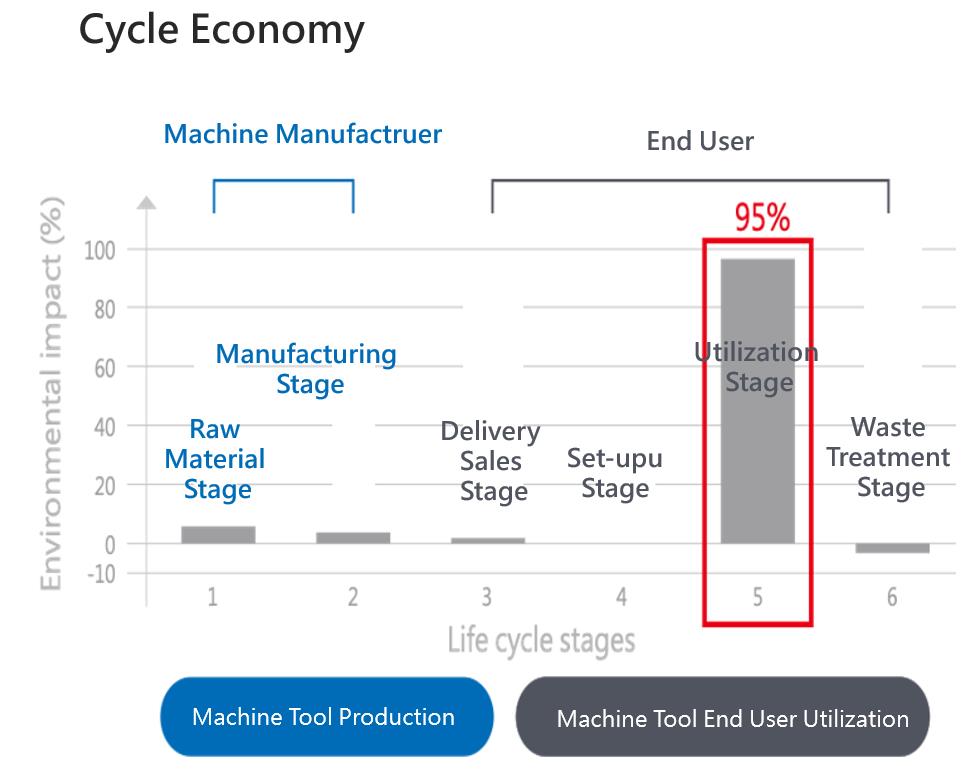
The right tool to evaluate energy efficiency of machine tools is: ISO 14955 The amount of energy supplied to a machine is not an adequate indicator of its energy efficiency, especially in the case of complex products like machine tools. To determine the energy efficiency of a machine tool, energy consumption needs to be considered against the results achieved – for instance, the number of workpieces produced, their shape, quality, accuracy and other relevant factors that are determined by the specific application.
AXILE Digital Intelligent energy management can help you optimize daily power consumption
AXILE R&D team has not been waiting for the peaks in energy costs to study how the measurement of machine tool power consumption could be monitored and improved. Needless to say that only what can be measured is subject to enhancing.
The ART™ Energy Management application which was launched a few years ago delivers round-the-clock monitoring of each machine’s energy consumption and usage conditions, providing the data required to optimize energy efficiency.
AXILE machines comply with ISO 14955 standards for the environmental evaluation of machine tools.
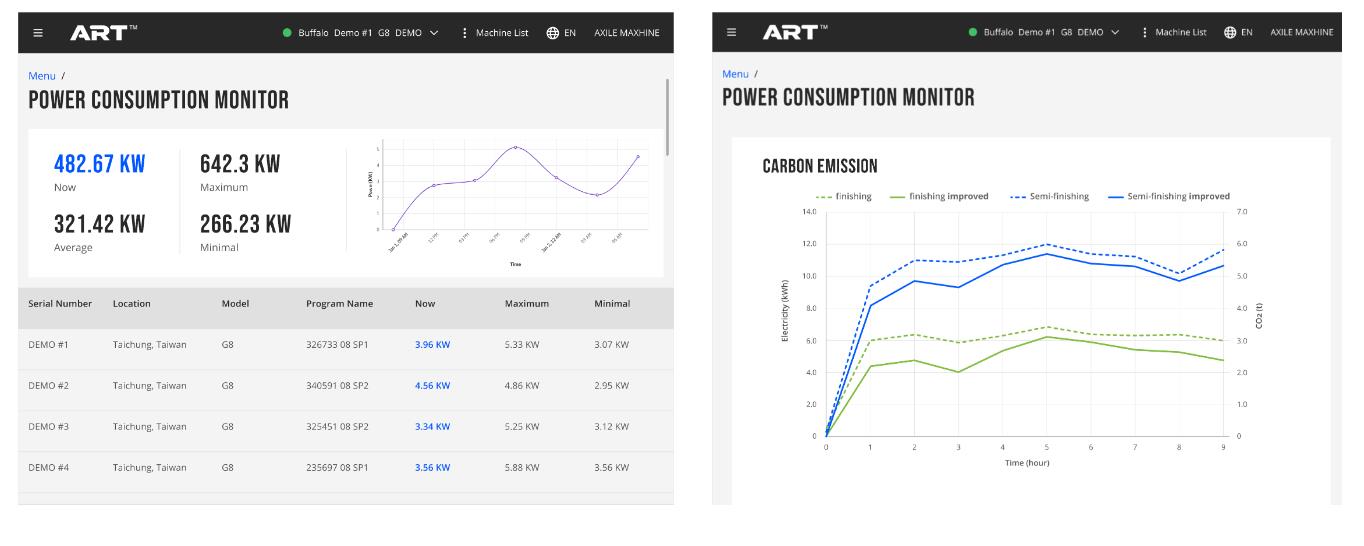
The above app monitors and reports the energy usage and efficiency of each individual machine, delivering information to users in an intuitive format. Based on strategies derived from this data, machinists can make daily adjustments to machine operations to achieve maximum energy efficiency and lower costs while reducing carbon emission for each workpiece being produced on AXILE machine tools.
Digital intelligent machines equipped with ART™ can perform statistics, analysis to improve processing conditions for operators and managers to understand the machine performance and take the immediate actions to optimize the machine utilization and its power efficiency.



